13 Degree C To F
sportsmenna
Sep 19, 2025 · 6 min read
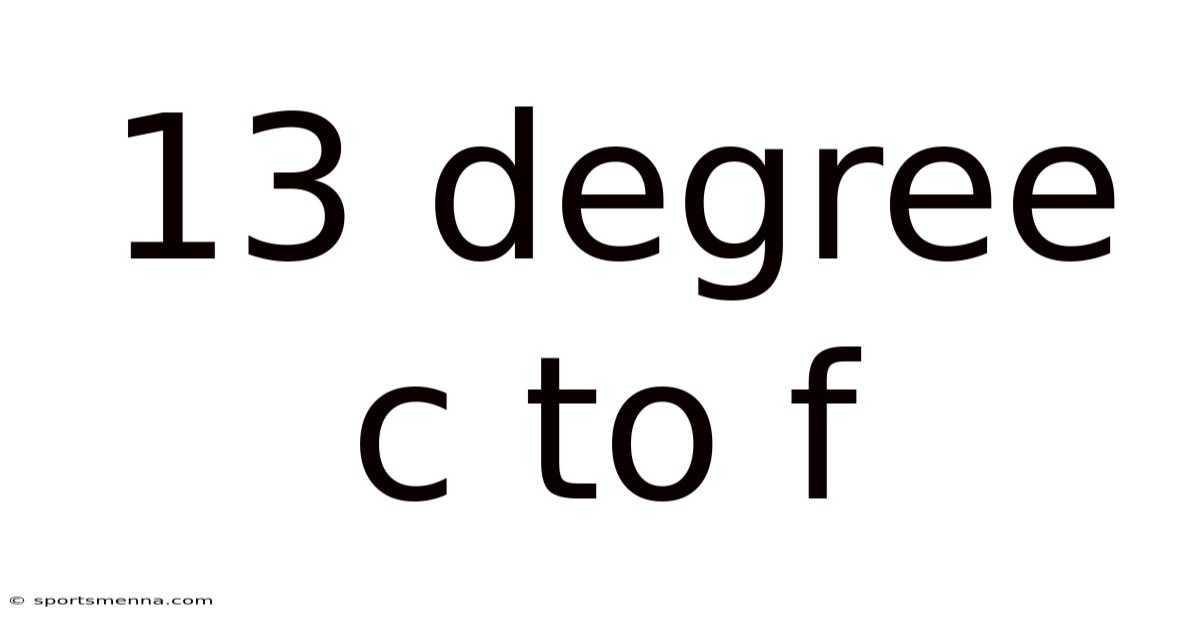
Table of Contents
Converting 13°C to Fahrenheit: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in many fields, from cooking and everyday life to scientific research and engineering. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of converting 13 degrees Celsius (°C) to Fahrenheit (°F), explaining the underlying formula, providing step-by-step instructions, exploring the historical context of these scales, and answering frequently asked questions. We'll delve into the practical applications of this conversion and highlight the importance of accurate temperature measurements.
Understanding Celsius and Fahrenheit
Before diving into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales involved: Celsius and Fahrenheit.
-
Celsius (°C): Also known as the centigrade scale, Celsius is based on the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. It's the most widely used temperature scale globally, primarily within the scientific community and everyday life in most countries.
-
Fahrenheit (°F): Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, Fahrenheit is still commonly used in the United States. Its reference points were initially based on a brine solution's freezing point and the human body temperature, resulting in water freezing at 32°F and boiling at 212°F.
The Conversion Formula: From Celsius to Fahrenheit
The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
This formula establishes a linear relationship between the two scales, allowing for accurate conversion between them. Let's break down each component:
- °C: This represents the temperature in degrees Celsius. In our case, this is 13°C.
- 9/5: This fraction is the conversion factor, reflecting the difference in the size of a degree between the two scales. One degree Fahrenheit is smaller than one degree Celsius.
- + 32: This constant accounts for the difference in the zero points of the two scales. Fahrenheit starts at 32°F where Celsius starts at 0°C.
Step-by-Step Conversion of 13°C to Fahrenheit
Now, let's convert 13°C to Fahrenheit using the formula:
-
Substitute the Celsius value: Replace °C with 13 in the formula: °F = (13 × 9/5) + 32
-
Perform the multiplication: Multiply 13 by 9/5: 13 × 9/5 = 23.4
-
Add 32: Add 32 to the result: 23.4 + 32 = 55.4
-
Final Result: Therefore, 13°C is equal to 55.4°F.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Accurate temperature conversions are vital in numerous fields:
-
Cooking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Being able to convert between the two ensures accurate cooking results, especially for baking where precise temperatures are critical.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is often measured in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. Understanding the conversion is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals monitoring their health.
-
Science and Engineering: Scientific experiments and engineering projects often require precise temperature control. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for ensuring consistency and accuracy across different experimental settings or international collaborations.
-
Meteorology: Weather reports may use either Celsius or Fahrenheit, depending on the region and target audience. Converting between these scales allows for easy understanding regardless of the reporting scale.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes require precise temperature control, such as manufacturing, chemical processing, and food processing. Accurate conversions are essential for maintaining quality and safety.
Historical Context of Temperature Scales
Understanding the historical development of Celsius and Fahrenheit provides context to their differences:
-
Fahrenheit Scale: Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, the scale was initially based on three reference points: the freezing point of a brine solution (0°F), the freezing point of water (32°F), and human body temperature (around 96°F). The scale was later refined, leading to the current standard freezing and boiling points of water.
-
Celsius Scale: Originally called the centigrade scale, it was proposed by Anders Celsius in 1742. Celsius's initial scale had 0°C as the boiling point of water and 100°C as the freezing point. This was later reversed to the current convention. The scale's simplicity and logical reference points made it widely adopted internationally.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature's Impact
Temperature plays a fundamental role in numerous physical and chemical processes. Understanding how temperature affects matter, such as its state (solid, liquid, gas), density, and reactivity, is critical across scientific disciplines.
-
Thermal Expansion: Materials expand when heated and contract when cooled. This principle is applied in various applications, including the design of bridges and buildings to account for temperature fluctuations.
-
Phase Changes: Temperature governs phase transitions between solid, liquid, and gaseous states. Understanding these transitions is fundamental to fields like chemistry and materials science.
-
Chemical Reactions: Temperature significantly influences the rate of chemical reactions. Higher temperatures often accelerate reactions, while lower temperatures can slow them down.
-
Biological Processes: Temperature has a critical role in biological processes, affecting enzyme activity, metabolic rates, and organism survival. Maintaining optimal temperatures is vital for many biological systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the conversion factor 9/5?
A: The factor 9/5 reflects the relative sizes of a degree Fahrenheit and a degree Celsius. A 1°C change is equal to a 9/5°F change because the range between the freezing and boiling points of water (100°C) is equal to 180°F (212°F - 32°F).
Q: Can I use online converters for Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, many online converters are available that can quickly perform this conversion. However, understanding the underlying formula is still beneficial for appreciating the mathematical relationship between the two scales.
Q: Are there other temperature scales besides Celsius and Fahrenheit?
A: Yes, other scales exist, such as Kelvin (K), which is an absolute temperature scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the lowest theoretical temperature possible. Kelvin is widely used in scientific applications. Rankine (°R) is another absolute scale used in some engineering fields.
Q: What is the significance of absolute zero?
A: Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which all molecular motion ceases. It represents the lowest possible temperature and is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics and physics.
Q: Is there an easy way to remember the conversion formula?
A: While memorizing the formula is the most accurate approach, some find it helpful to break it down into manageable steps or use mnemonics. The important part is understanding the underlying process, not just rote memorization.
Conclusion
Converting 13°C to 55.4°F is a straightforward process using the established formula. However, this conversion transcends a simple mathematical exercise. It highlights the importance of understanding different temperature scales and their applications across various fields. By grasping the principles behind the conversion, we gain a deeper appreciation for the role temperature plays in shaping our world, from everyday experiences to complex scientific endeavors. Accurate temperature measurement and conversion are crucial for ensuring safety, precision, and understanding across numerous disciplines, reinforcing the importance of mastering this essential skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Edges In Cylinder
Sep 19, 2025
-
Feet Per Second To Joules
Sep 19, 2025
-
How Many Lbs Is 9kg
Sep 19, 2025
-
Time Difference Mauritius To Uk
Sep 19, 2025
-
What Metal Is The Lightest
Sep 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 13 Degree C To F . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.